EPOS Architecture
The EPOS architecture is based on four main elements, which
compose its legal, financial and operational backbone (Fig. 1). At the bottom of
the chain the National Research Infrastructures (NRI) provide
data through their respective Thematic Core Service (TCS),
i.e. a thematic community that develops data and services that are specific for
a subdiscipline of solid Earth science. The TCSs act as a middle layer before
the data and services are eventually integrated by the Integrated Core Services
(ICS) into a single, multidisciplinary data portal accessible
for all users. The TCS-ICS federated system is the skeleton of the
'EPOS Delivery Framework' and represents the solution for
integrating distributed infrastructures via shared standards for data and
metadata (Fig. 1). The EPOS ERIC
governs and oversees this entire process.
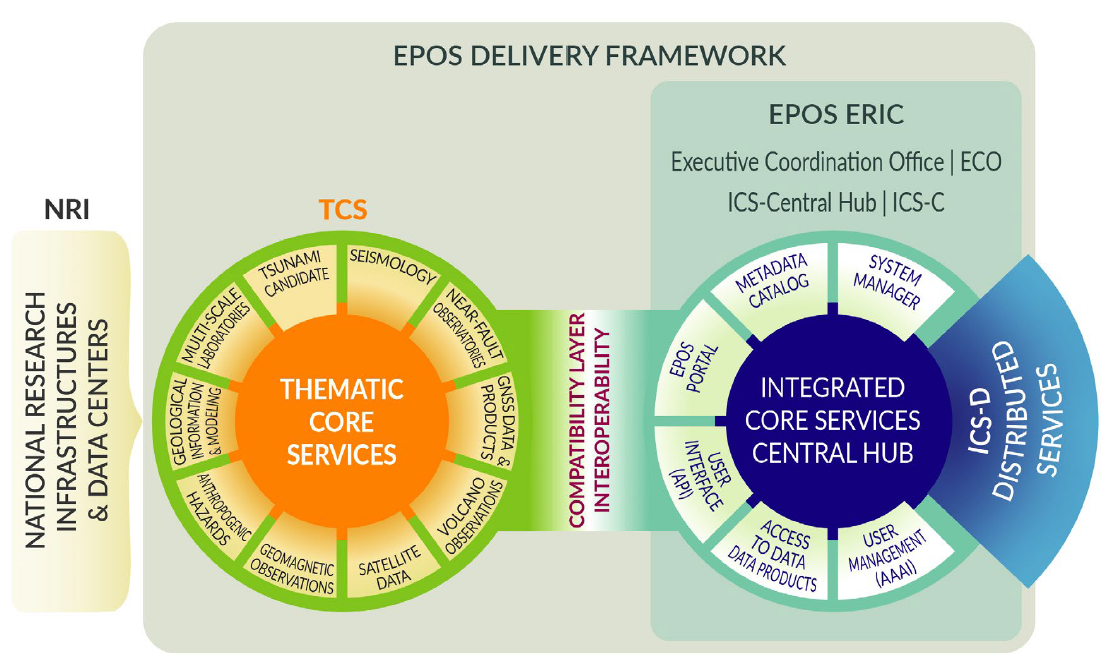 Fig. 1. The EPOS Architecture and its 4 components: the National
Research Infrastructures (NRI), the Thematic (TCS) and Integrated (ICS) Core
Services, of which the latter two compose the EPOS Delivery Framework. The ICS
and the Executive Coordination Office (ECO) fall under the EPOS ERIC legal subject.
This figure was provided by EPOS ERIC.
Fig. 1. The EPOS Architecture and its 4 components: the National
Research Infrastructures (NRI), the Thematic (TCS) and Integrated (ICS) Core
Services, of which the latter two compose the EPOS Delivery Framework. The ICS
and the Executive Coordination Office (ECO) fall under the EPOS ERIC legal subject.
This figure was provided by EPOS ERIC.
National Research Infrastructures (NRI)
The NRIs represent the foundations of the EPOS architecture. They are existing
and operational organizations, which provide high-quality earth science data and
services at a national level for the different geoscience communities. NRIs
contributing to EPOS are owned and managed at a national level.
Thematic Core Services (TCS)
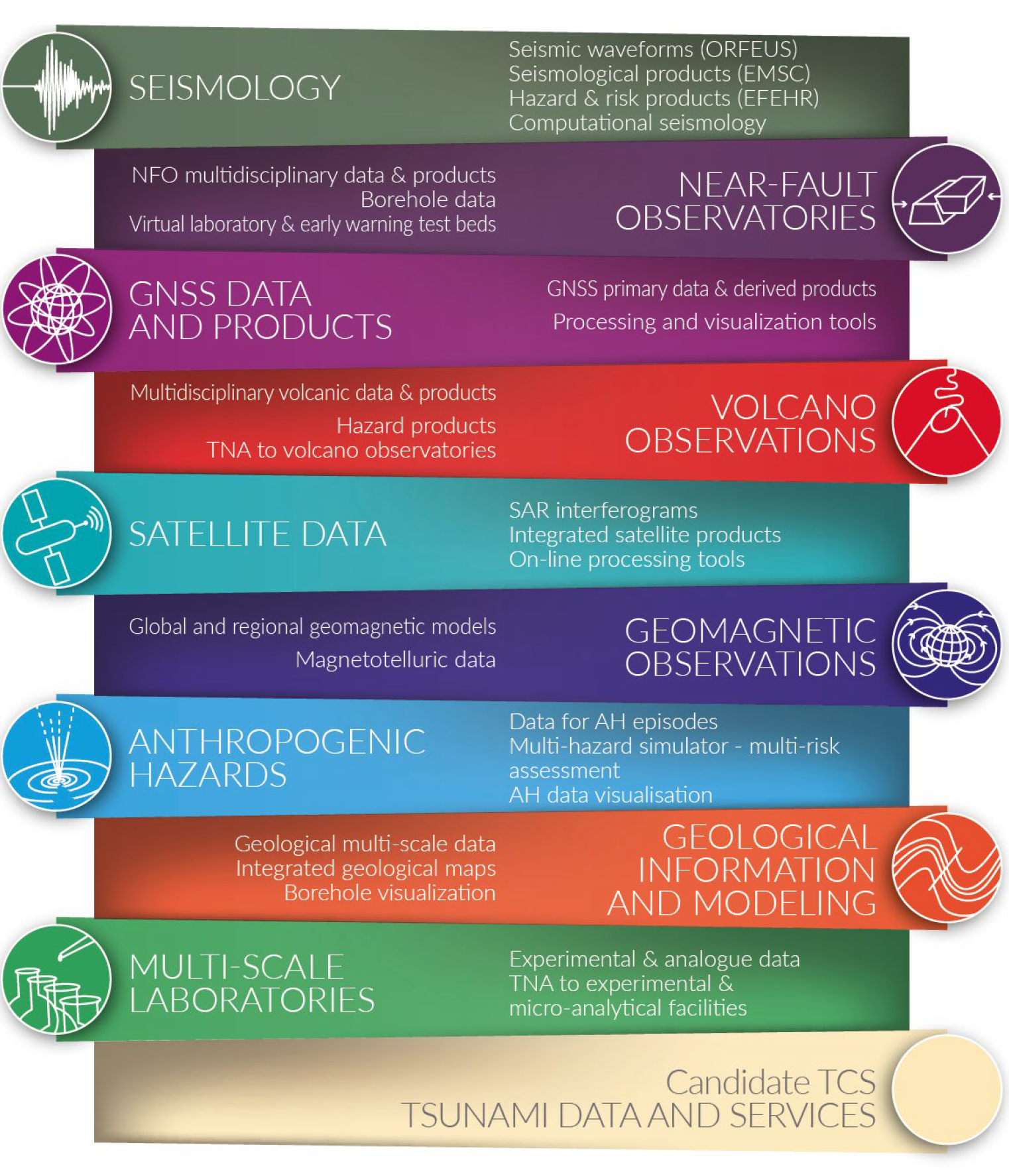 Fig. 2. The 10 Thematic Core Services currently integrated into EPOS. Figure taken from Cocco et al. (2022).
Fig. 2. The 10 Thematic Core Services currently integrated into EPOS. Figure taken from Cocco et al. (2022).
The TCSs represent the
transnational governance level of the different thematic communities
contributing to EPOS. They ensure the management, standardization, and quality
control of the data and metadata produced by the NRIs to ensure integrated
access through the ICS. Each TCS coordinates a number of service providers,
i.e. organizations that are responsible for the key TCS services. These services
primarily consist of providing harmonized access to the data through
standardized web APIs available from TCS community portals and data nodes. The
TCS are governed by consortia that are linked to the EPOS ERIC via legal
collaboration agreements.
Currently, the following thematic communities exist (Fig. 2):
Currently, the following thematic communities exist (Fig. 2):
- Seismology
- Near-Fault Observatories
- GNSS Data and Products
- Volcano Observations
- Satellite Data
- Geomagnetic Observations
- Anthropogenic Hazards
- Geological Information and Modeling
- Multi-Scale Laboratories
- Tsunami (Candidate TCS)
More detailed information on the scientific expertise, data and services
provided by these thematic communities can be found by clicking the
corresponding hyperlinks.
Integrated Core Services (ICS)
The ICS, which stands at the core of the EPOS e-infrastructure, is the platform
where all heterogeneous data and services are integrated, ensuring
interoperability with the data and services provided by the TCSs. The ICS system
architecture has been designed to provide the tools to facilitate the discovery of
Data, Data products, Software and Services (DDSS) and the
integration of these resources to fulfil users requests across the EPOS community.
The ICS consists of a Central (ICS-C) and
Distributed (ICS-D) hub. The former provides the user access to
all multidisciplinary data and products made available by the TCSs through the
newly launched EPOS Data Portal,
while the latter aims to be a virtual research environment that will give access
to external tools for services as computation, visualization and modelling.
ICS-D pilot implementations are currently in progress. More information on the
architecture of the Integrated Core Services can be found
here.
The following videos give a tutorial on how to access and use the EPOS Data Portal:
The following training session goes into more depth on how to apply the EPOS Data Portal in research/education:
EPOS ERIC (European Research Infrastructure Consortium)
To govern the integration of the above elements and to coordinate the long-term
integration of research infrastructures for solid Earth science in Europe, EPOS
was established as an ERIC in 2018. An ERIC is a legal entity that facilitates
the development and operation of research infrastructures with a pan-European
dimension. ERIC receives financial contributions from the above member countries
to support its working. More information on the legal structure of EPOS ERIC and
its members can be found
here.
